Air-Brake Coil Hose — Technical Guide and Product Overview
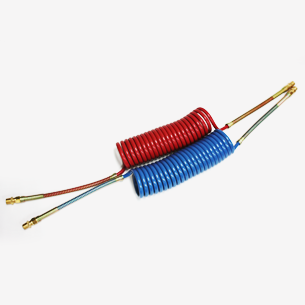
Product: Air-Brake Coil Hose (B-type, SAE J844D / DIN 74323)
Sizes: 3/8″ (model 3/8) and 1/2″ (model 1/2)
Supply: Sold by the roll for automotive and commercial vehicle pneumatic systems
Introduction
The Air-Brake Coil Hose is a purpose-built, coiled pneumatic hose designed to connect compressed-air circuits on trucks, trailers and other heavy vehicles where compact, flexible interconnections are required. Offered in B-type construction and manufactured to comply with SAE J844D and DIN 74323, this product balances high-pressure capability, repeated flex life and compact storage. It is optimized for vehicle air-brake applications—including tractor/trailer lines and auxiliary pneumatic circuits—where reliable air delivery, mechanical resilience and long service life are mandatory.
This technical article presents an in-depth overview of the Air-Brake Coil Hose: its technical functions and applications, specifications and dimensional data, materials and build quality, key features, use cases, comparisons with alternative hose types, benefits and limitations, recommended maintenance and care, and selection guidelines for system designers and maintenance engineers.
Technical Overview
The Air-Brake Coil Hose is a tension-compressed, helically coiled pneumatic hose that deploys and retracts like a spring. Its geometry reduces slack and prevents long runs of loose hose from dragging or snagging on vehicle undercarriage and road debris. Coiled hoses are frequently applied between moving vehicle elements (tractor/trailer, drawbar, or adjustable couplings) where variable separation exists but space and hose management are important.
Key technical attributes of the Air-Brake Coil Hose include:
- Coiled geometry: Reduces storage footprint when disconnected and limits free-hanging length while providing controlled extension when the vehicle articulates.
- B-type construction: Conforms to specific performance provisions in SAE J844D and DIN 74323 (see Standards section below).
- Pressure capability: Designed for continuous service up to a maximum usage pressure of 25 kgf/cm² (nominal), with a manufacturer’s rated burst pressure of 100 kgf/cm² at 20 °C—providing a 4:1 safety factor between burst and rated working pressure.
- Flexible operation over a practical temperature range: Materials and compound choices maintain flexibility and sealing performance under typical ambient conditions encountered by commercial vehicles.
Standards and Compliance
This B-type Air-Brake Coil Hose is produced to meet the requirements of:
- SAE J844D: The SAE J844 standard series specifies performance criteria for automotive compressed-air hoses used in brake and pneumatic systems. Requirements typically include dimensional tolerances, burst and working pressure tests, low- and high-temperature performance, resistance to ozone and aging, and identification/marking. The “D” revision indicates the current specification at the time of manufacture.
- DIN 74323: The German standard for vehicle pneumatic hoses, covering materials, construction and performance tests relevant to vehicle braking applications. Compliance demonstrates suitability for European-style assemblies and regulatory alignment for fleets operating to DIN-based guidelines.
Compliance to these standards gives fleet engineers and maintenance managers the assurance that the hose has been manufactured and tested to recognized automotive performance criteria, suitable for demanding service conditions.
Specifications and Dimensions
The following table summarizes the manufacturer’s nominal geometry and pressure performance for the two available models of the Air-Brake Coil Hose. All pressure values are those declared by the manufacturer at a reference temperature of 20 °C.
| Model | Nominal Size | Outer Diameter (O/D) | Inner Diameter (I/D) | Burst Pressure (20 °C) | Maximum Usage Pressure (20 °C) | Minimum Curvature Radius | Nominal Linear Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MODEL 3/8 | 3/8″ | 9.5 mm | 7.0 mm | 100 kgf/cm² (≈ 9.81 MPa / 1,423 psi) | 25 kgf/cm² (≈ 2.45 MPa / 356 psi) | 45 mm | 60 g/m (nominal) |
| MODEL 1/2 | 1/2″ | 12.7 mm | 9.5 mm | 100 kgf/cm² (≈ 9.81 MPa / 1,423 psi) | 25 kgf/cm² (≈ 2.45 MPa / 356 psi) | 29 mm | 68 g/m (nominal) |
Notes: The burst pressure and maximum usage pressure are manufacturer-rated at 20 °C and provide conservative values for safe operation. The burst-to-working ratio of 4:1 conforms to common design practice for pneumatic hoses within automotive brake systems. Minimum curvature radius is the smallest static bend radius for the coiled hose to avoid kinking or excessive stress on the material; repeated dynamic bending should be minimized below this radius.
Materials and Build Quality
Air-brake coil hoses must perform in mechanically demanding and chemically aggressive environments: exposure to ozone, diesel fuel, hydraulic fluids, road salts, mechanical abrasion, and repeated flexing. Therefore, material selection, compound formulation and the manufacturing process are critical for long-term reliability.
Typical Materials and Compound Options
Although specific material formulations vary by manufacturer and product line, Air-Brake Coil Hoses for vehicle brake systems are typically constructed from one of the following elastomeric systems or blends:
- Polyurethane (TPU/PU): High tensile strength and excellent abrasion resistance; excellent memory for coiling; good flexibility across a wide temperature range; resistant to kinking and common oils. Common for commercial coiled air lines where coil retention and abrasion resistance are priorities.
- Synthetic rubber compounds (e.g., EPDM, NBR blends): Good resistance to heat, ozone, aggressive weathering and many hydraulic fluids. EPDM offers outstanding ozone and weather resistance; NBR adds fuel and oil resistance where required. Rubber compounds can be reinforced to achieve desired burst characteristics.
- Hybrid thermoplastic-rubber formulations: Designed to combine the flexibility and memory of TPU with the chemical resistance of rubber. These compounds may be used to tune specific mechanical properties such as low-temperature flexibility and abrasion resistance.
For the product presented here — a B-type coil hose conforming to SAE J844D and DIN 74323 — it is common to see either polyurethane or a specially formulated synthetic rubber compound. The exterior finish is typically smooth, with a visible coil memory and a color or identification stripe for quick field recognition.
Reinforcement and Construction
To achieve the stated burst pressure while retaining flex life, manufacturers use reinforcement strategies such as:
- Textile plies: High-strength woven fibers embedded in the elastomer to resist radial expansion under pressure while maintaining flexibility.
- Helical reinforcement: In some constructions, a helix or braid of stiff fibers or plastics is incorporated to support the coiled geometry and maintain axial strength.
- Layered extrusion: Multi-layer extruded constructions (inner liner, reinforcement layer, outer cover) ensure chemical compatibility at the air interface, mechanical strength, and abrasion/ozone resistance on the exterior.
Manufacturing and Quality Controls
Manufacturing processes for these hoses include precision extrusion for the core profile, coiling under controlled tension, heat-setting to establish the coil memory, and post-cure or stabilization stages. Quality controls typically include:
- Dimensional verification (I/D, O/D, wall thickness)
- Hydrostatic/burst testing at 20 °C to validate burst pressure and identify defects
- Flex-fatigue cycling to evaluate long-term flex life and memory retention
- Ozone, aging and abrasion tests per standardized laboratory methods referenced by SAE or DIN
- Visual and leakage inspections for each production batch
Key Features
The Air-Brake Coil Hose delivers a number of engineered features tailored for vehicle air-brake systems. Highlights include:
- Compact coiled geometry: Reduces slack and snag risk while allowing controlled extension and retraction between vehicle units.
- Certified performance: Manufactured to meet SAE J844D and DIN 74323 requirements for pneumatic brake hose performance.
- High burst rating: 100 kgf/cm² burst pressure (20 °C) with a maximum usage pressure of 25 kgf/cm², providing a 4:1 safety margin.
- Two common sizes: 3/8″ and 1/2″ internal diameter options to match a wide range of vehicle service needs and flow requirements.
- Good flex life and memory: Materials and heat-set coiling provide repeatable retraction characteristics for many cycles.
- Ozone and weather resistance: Compound selection and outer cover formulation optimize resistance to ozone cracking and road conditions.
- Supplied by roll: Rolls facilitate easier inventory management for maintenance shops and OEM assembly lines; lengths per roll can be specified at order.
Use Cases and Applications
Air-Brake Coil Hoses are an integral component in numerous vehicle pneumatic systems. Typical applications include:
- Tractor–trailer air connections: Coiled service and emergency lines between tractors and trailers where variable separation occurs during turns and coupling/uncoupling operations.
- Dump truck and trailer interfaces: Retractable connections for trailers that separate or adjust in length during operations.
- Urban transit and bus doors: Short coiled connections for pneumatic door actuation or flexible connections within the vehicle where compact routing is needed.
- Construction and off-highway vehicles: Compact connections for air suspension components or accessory pneumatic tools where coil management reduces trip hazards and snagging.
- Fleet maintenance spares: Sold by the roll for garage repair shops, enabling custom-length assembly and field repairs with retained coiled geometry.
Because the hoses conform to SAE and DIN performance criteria, they fit into established fleet maintenance and supply-chain practices for heavy-duty vehicles worldwide.
Comparison with Other Hose Types
When selecting a hose for a vehicle pneumatic application, engineers and maintenance teams routinely choose between several hose classes. The table below compares the Air-Brake Coil Hose to common alternatives: a straight rubber air hose, a polyurethane spiral coil hose, and a thermoplastic corrugated hose. The comparison highlights attributes most relevant to vehicular air-brake systems.
| Attribute | Air-Brake Coil Hose (B-type) | Straight Rubber Air Hose | Polyurethane Spiral Coil Hose | Thermoplastic Corrugated Hose |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geometry | Coiled (compact, retracting) | Straight (flexible) | Spiral coil (very high memory) | Corrugated/tubular (flexible but bulky) |
| Typical Applications | Tractor/trailer connections, short retracting runs | General air distribution, fixed runs | Hand tools, short retracting tool lines | Space-constrained flexible routing; liquid/air hybrid |
| Burst / Working Pressure | 100 / 25 kgf/cm² (manufacturer rated) | Varies (lower burst ratio unless reinforced) | Moderate; designed for lower pressure tool lines | Moderate, depends on wall thickness and reinforcement |
| Abrasion Resistance | High (typical elastomer/PU outer cover) | Good (rubber cover), varies with compound | Excellent (PU highly abrasion resistant) | Moderate, outer cover prone to abrasion |
| Flex Memory | Good — retains coils reliably | Poor — stays extended unless managed | Excellent — strong retracting force | Low — tends to remain in bent positions |
| Ease of Installation | Moderate — requires appropriate fittings | Easy — direct routing or clamps | Easy — light and compact for tools | Easy — flexible routing but bulkier |
| Cost | Moderate | Low to moderate | Low to moderate | Moderate to high |
This comparison emphasizes that the Air-Brake Coil Hose occupies the middle ground between specialized spiral tool hoses and generic straight rubber hoses: it offers certified pressure performance, coiling memory, and abrasion resistance that is particularly suited for vehicle brake interconnections.
Benefits and Limitations
Benefits
- Compact storage and controlled slack: The coiled design prevents long lengths of hose from dragging or entangling on moving vehicle components.
- Regulatory compliance: Conformance to SAE J844D and DIN 74323 assures standardized performance and simplifies qualification in fleet operations.
- High pressure capability with safety margin: The rated burst pressure gives a robust safety factor for transient events and pressure spikes.
- Excellent abrasion and weather resistance: Proper compound and cover formulations extend field life in harsh conditions.
- Ease of inventory: Supplied by the roll, enabling custom-length fabrication and fewer SKU requirements for stockrooms.
Limitations
- Length limitations when extended: Coiled hoses provide extension only up to a designed maximum; they are not intended to replace long straight runs.
- Potential for fatigue at extreme articulation: Repeated bending below the minimum curvature radius or exposure to highly cyclic articulation can reduce service life.
- Temperature and chemical compatibility: Although compounds are selected for broad resistance, extreme environments (very high temperatures above the material rated range or exposure to incompatible solvents) may degrade performance—verify with the manufacturer for specific environments.
- Serviceability of fittings: The connection ends (fitted or crimped) are points of potential failure and must be installed and inspected per good practices to ensure leak-free operation.
Understanding these trade-offs allows engineers to apply Air-Brake Coil Hoses where their advantages are most relevant—interconnection of moving components and short, retractable pneumatic circuits—while planning for replacement intervals and protective measures in high-demand contexts.
Selection and Installation Guidance
Appropriate selection, routing and installation of air-brake coil hoses are critical for system reliability. The following guidance is intended for engineers, fitters and maintenance technicians responsible for specifying and fitting these hoses.
How to Choose Between 3/8″ and 1/2″
- Flow requirements: Use 1/2″ internal diameter where higher flow capacity or lower pressure drop over the hose is required—common for longer connections or systems where rapid pressure equalization is needed.
- Packaging and space: Consider the O/D and coiled profile—3/8″ has a smaller O/D (9.5 mm) and will take up less space on reels or in routing channels.
- Weight and flexibility: The 3/8″ model is slightly lighter per linear meter; however, the 1/2″ model typically provides a higher volumetric flow for the same pressure drop.
- Compatibility: Match to existing fittings and connectors commonly found on the vehicle (glad hands, push-in fittings, 7/16″-20 UNF or other standards). Adaptors may be used but add potential leak points—prefer direct matches.
Installation Best Practices
- Inspect before fitting: Check hoses for visible defects, contamination, or damage. Do not install hoses with nicks, cuts or delamination.
- Correct end fittings: Use manufacturer-recommended fittings and clamps. For crimped terminations, ensure tooling is calibrated to produce a proper crimp pattern and compressive force.
- Maintain minimum curvature radius: Route the hose so no portion is bent below the stated minimum curvature radius to avoid stress concentrations and early fatigue.
- Provide strain relief: Use clamps or anchor points to prevent the hose from being pulled at the fitting during vehicle articulation or coupling operations.
- Avoid tight abrasion points: Protect the hose against rubbing on sheet metal, edges or other components using sleeves or protective conduit.
- Secure routing: Keep the hose clear of abrasive surfaces, heat sources (exhausts), and rotating components. Use tie straps designed for pneumatic lines at recommended spacing.
- Pressure test after installation: Perform a leak check and a system pressure check at an appropriate safety margin to confirm the assembly integrity.
Testing, Inspection and Maintenance Guide
Reliable performance of air-brake systems hinges on regular inspection and scheduled maintenance of hoses and fittings. The Air-Brake Coil Hose should be part of a documented maintenance program that follows regulatory and fleet-specific intervals.
Routine Inspection Checklist (daily/weekly)
- Visual check for cuts, abrasions, bulges or surface cracking.
- Confirm coil retracts properly and is not permanently elongated or deformed.
- Inspect fittings for corrosion, looseness or visible leakage.
- Ensure hose routing remains secure and tied where required.
Periodic Detailed Inspections (monthly/quarterly)
- Perform an operational pressure test—monitor for pressure loss that may indicate small leaks.
- Check the hose along its length for stiffness changes, soft spots or blistering—signs of internal degradation.
- Verify that minimum curvature radii are maintained under all operating conditions; adjust routing if the hose is repeatedly flexed below the stated radius.
Replacement Criteria and Intervals
- Replace immediately if you find cracks, steady leakage, bulging or significant abrasion down to underlying reinforcement.
- Replace any hose that fails a pressure proof or burst test.
- Establish interval-based replacement policy as part of fleet management—many operators use a multi-year inspection/replacement cycle (e.g., 3–5 years) adjusted to duty cycle, environment, and observed failure rates.
Pressure Testing and Proofing
Pressure testing should align with manufacturer recommendations and the referenced standards. Typical practice includes:
- Proof testing: Apply a pressure at or slightly above the maximum usage pressure (e.g., 1.25× working pressure) to validate assembly integrity without overstressing the hose.
- Burst testing (factory): Performed to validate manufacturing quality—manufacturer-rated burst is 100 kgf/cm² at 20 °C.
- On-vehicle checks: Leak testing using soapy water or ultrasonic leak detectors for assembled systems under working pressure.
Document all tests and record outcomes as part of service history—traceability aids root cause analysis for failures and provides compliance evidence for audits.
Handling, Storage and Shelf Life
Proper storage and handling preserve material properties and coil memory prior to installation:
- Storage environment: Store in a cool, dry location away from direct sunlight and sources of ozone (high-voltage equipment) and solvents. UV exposure accelerates degradation of some elastomers.
- Temperature: Avoid prolonged storage below -10 °C or above +40 °C unless specified by the manufacturer. Recondition hoses stored at low temperatures back to ambient before installation to avoid brittle behavior during fitting.
- Packaging: Keep the hose in supplied rolls or reels. Avoid compressing coils for extended durations as this may change the coil memory.
- Shelf life: Hoses can age in storage. A typical recommended shelf life for elastomeric hoses is 3–5 years under controlled storage, but this depends on compound and packaging. Check manufacturer guidance for guaranteed shelf life.
Failure Modes and Troubleshooting
Understanding common failure modes enables proactive mitigation. Key failure mechanisms include:
- Abrasion and cut-through: External damage due to rubbing or contact with sharp edges. Mitigate with protective sleeves, re-routing and proper tie-down.
- Ozone cracking and weathering: Surface cracking caused by ozone and UV exposure, aggravated by stress. Use ozone-resistant compounds and limit exposure.
- Fatigue at fittings: Repeated flexing at crimped or assembled ends can loosen fittings or create micro-leaks. Provide strain relief and use high-quality termination methods.
- Internal delamination: Separation between layers due to manufacturing defects or chemical attack; often results in bulging or local soft spots. Replace immediately if detected.
- Thermal degradation: Exposure to excessive heat can harden or embrittle the hose; avoid proximity to exhausts and hot surfaces.
Troubleshooting steps:
- Isolate the suspect assembly and perform a visual inspection for obvious damage.
- Pressure test the isolated section to determine whether the leak is at the hose or at the fitting.
- If the leak is at a fitting, verify correct part selection, installation torque and absence of cross-threading. Re-terminate with a new ferrule or fitting if necessary.
- Replace the hose if any signs of structural degradation are found; do not attempt splice repairs on primary brake service hoses.
Ordering, Customization and Supply
Air-Brake Coil Hoses are commonly supplied by the roll to enable customized length cutting and termination within maintenance facilities or OEM assembly lines. When placing orders, specify the following to ensure correct supply and compatibility:
- Model (3/8″ or 1/2″) and nominal inner diameter
- Roll length required (per roll length or total quantity)
- Environmental requirements (if extremes of temperature or chemical exposure are expected)
- End-fitting type and size, if factory-terminated assemblies are required (e.g., crimped ferrules, push-to-connect ends or flared ends)
- Required standard compliance documentation (e.g., certificate of conformity to SAE J844D / DIN 74323)
For large fleets or OEMs, request batch certification for burst testing and material traceability. Custom colors, identification stripes or printed markings can be specified for fleet identification or safety coding.
Practical Selection Example
Scenario: You manage a fleet of tractor-trailers that operate with standard single-conductor air brake systems. Your service department needs a retractable interconnect that can tolerate frequent short extensions during coupling and decoupling, resist abrasion on roadside operations, and minimize inventory complexity.
Recommendation:
- Choose the Air-Brake Coil Hose MODEL 3/8 if the vehicle’s air demand is moderate and you prefer a more compact feed on hose reels and reels. The 3/8″ I/D (7.0 mm) yields adequate flow for short service lines and has a smaller O/D (9.5 mm) for neat routing.
- If higher flow rate or faster pressure equalization is required—e.g., for systems with multiple trailers or larger volume reservoirs—select MODEL 1/2 (9.5 mm I/D) to reduce pressure drop during service application.
- Specify factory termination with compatible air fittings (match to glad-hand or union sizes) and request batch burst test certificates with the roll shipment.
Conclusion
The Air-Brake Coil Hose (B-type; SAE J844D / DIN 74323) provides a robust, compact, and standards-compliant option for vehicle pneumatic brake interconnections. Offered in 3/8″ and 1/2″ sizes, it delivers a 4:1 burst-to-working pressure margin, reliable coil memory for controlled extension and retraction, and construction choices that support abrasion and weather resistance. When selected and installed according to recommended practices—maintaining minimum curvature radii, using compatible fittings, and following inspection and replacement guidelines—the Air-Brake Coil Hose offers an effective balance of safety, serviceability and space efficiency for fleet operators and OEMs.
For fleet managers, specification engineers and maintenance technicians, this product is a practical choice where coiled geometry reduces trip and snag hazards, and compliance to SAE and DIN standards mitigates qualification risk. To maximize life and safety, combine the hose with a controlled inspection program, correct routing, and protective measures in high-abrasion zones.
Quick Reference — Key Technical Data (Summary)
- Models: MODEL 3/8 and MODEL 1/2
- Compliances: SAE J844D, DIN 74323
- Working pressure: 25 kgf/cm² (nominal at 20 °C)
- Burst pressure: 100 kgf/cm² (at 20 °C)
- Minimum curvature radius: 45 mm (3/8), 29 mm (1/2)
- Nominal linear weight: 60 g/m (3/8), 68 g/m (1/2)
- Supply format: Rolls (lengths customizable)
If you require datasheets, material certificates, test reports, or recommendations for end fittings and termination procedures for in-house assembly, request the manufacturer’s technical pack or contact your supplier for factory-terminated assemblies matched to your vehicle fittings and regulatory environment.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt






Reviews
There are no reviews yet.