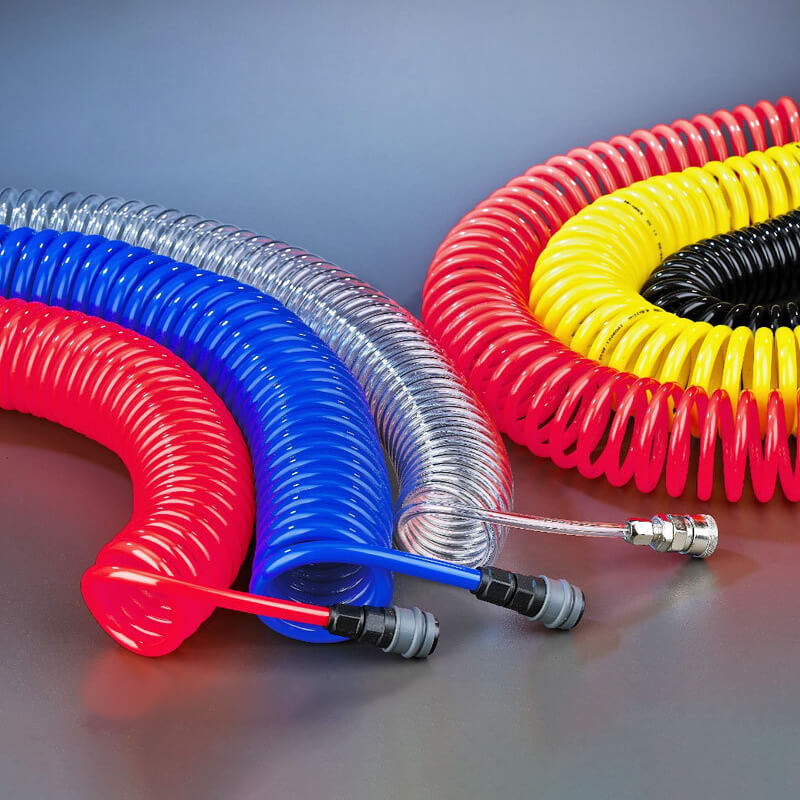
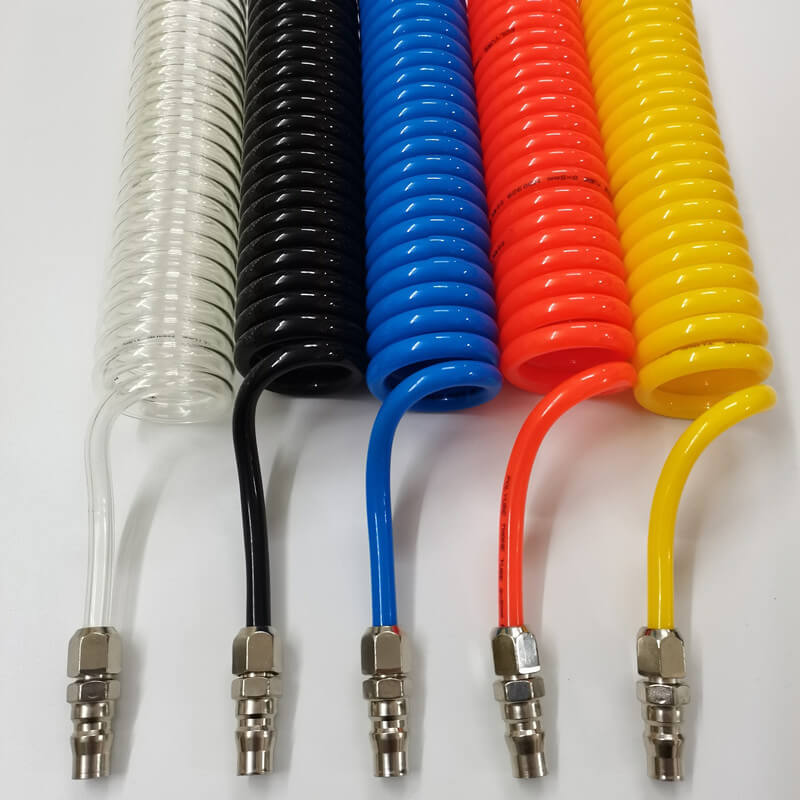
In the world of compressed air systems, hoses are not just a conduit — they are the lifelines that keep tools and machinery running smoothly. Among different hose designs, the spiral pneumatic hose (also called coiled air hose) stands out for its flexibility, compact storage, and durability.
From automotive workshops to industrial assembly lines, spiral hoses are everywhere. This article provides a comprehensive 2500-word guide to pneumatic spiral hoses: what they are, how they are built, the materials used, their advantages and disadvantages, and how to select and maintain them for long-term efficiency.
1. What is a Pneumatic Spiral Hose?
A pneumatic spiral hose is a compressed air hose designed in a coiled, spring-like shape. Unlike straight hoses, spiral hoses automatically retract after use, minimizing clutter and reducing the risk of tripping or hose damage.
They are commonly used with air tools, blow guns, spray guns, pneumatic cylinders, and robotic arms, where both flexibility and space-saving are crucial.
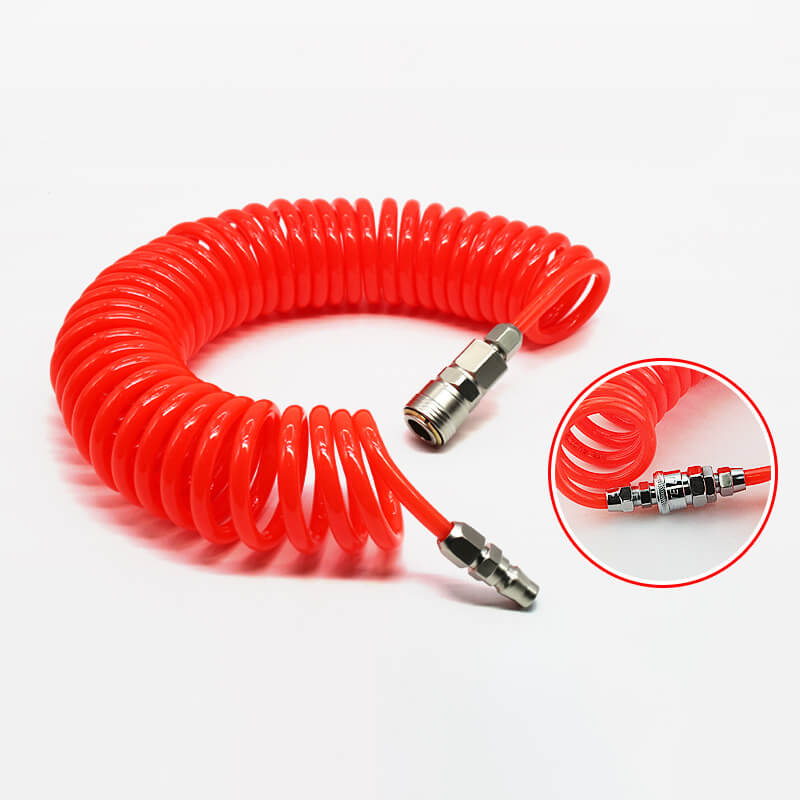

2. Structure and Design Features
A spiral pneumatic hose typically consists of:
-
Core Tube: Made from PU (Polyurethane), PA (Nylon), or PE (Polyethylene).
-
Spiral Forming: Thermally set into a spring coil to provide elasticity and memory.
-
End Fittings: Usually brass, stainless steel, or nickel-plated connectors (male/female thread, quick couplers).
-
Protective Sleeves: At each end to prevent kinking where the hose meets the fitting.
Design Benefits:
-
Self-retracting, saving space
-
Lightweight and portable
-
Prevents tangling or knotting
-
Withstands bending without cracking

3. Materials Used in Spiral Pneumatic Hoses
a) Polyurethane (PU) Spiral Hoses
-
Extremely flexible, even in low temperatures
-
Excellent abrasion resistance
-
Light and easy to handle
-
Common in workshops and handheld air tools
b) Polyamide (PA / Nylon) Spiral Hoses
-
Stronger and more pressure-resistant
-
Slightly less flexible than PU
-
High chemical and oil resistance
-
Preferred in industrial and automotive applications
c) Polyethylene (PE) Spiral Hoses
-
Lightweight and economical
-
Suitable for low-pressure applications
-
Stiffer, less flexible than PU or PA
d) Hybrid Materials
Some manufacturers combine materials (e.g., PU outer with nylon reinforcement) for better balance between flexibility and strength.

4. Advantages of Pneumatic Spiral Hoses
-
Compact and Space-Saving
-
Automatically retracts when released
-
Reduces floor clutter in workshops
-
-
Safety
-
Coiled design minimizes tripping hazards
-
Less chance of damage from dragging on rough surfaces
-
-
Flexibility
-
Can stretch several times its coiled length
-
Suitable for dynamic movement with air tools or robotics
-
-
Durability
-
Resistant to abrasion, oils, and chemicals
-
Long service life in industrial environments
-
-
Ease of Handling
-
Lightweight, ergonomic, and user-friendly
-
Compatible with quick-connect fittings
-

5. Limitations of Spiral Hoses
-
Limited Length: Not ideal for very long-distance air supply
-
Pressure Drops: More likely if stretched excessively
-
Stiffness in Some Materials: Nylon and PE are less flexible
-
End Wear: Stress at connectors may cause leaks if not reinforced
-
Not Suitable for Hydraulic Systems: Only for pneumatic and low-pressure fluids
6. Types of Pneumatic Spiral Hoses
a) By Material
-
PU Spiral Hoses – best for flexibility
-
Nylon Spiral Hoses – best for strength and pressure
-
PE Spiral Hoses – budget-friendly
b) By Diameter
-
Small Bore (4mm, 6mm ID): for precision tools, lab equipment
-
Medium Bore (8mm, 10mm ID): general pneumatic tools
-
Large Bore (12mm, 16mm ID): heavy-duty, high-flow tools
c) By Application
-
Standard air delivery
-
High-pressure spiral hoses (reinforced)
-
Anti-static spiral hoses (for electronics)
-
Food-grade spiral hoses (FDA compliant)

7. Applications of Spiral Pneumatic Hoses
-
Automotive Workshops
-
Air impact wrenches, tire inflators, spray painting
-
-
Industrial Assembly Lines
-
Pneumatic tools, pick-and-place machines, cylinders
-
-
Robotics and Automation
-
Flexible connections for moving arms
-
-
Construction Sites
-
Portable air compressors and nail guns
-
-
Food & Beverage Industry
-
Special FDA-approved PU spiral hoses for clean air supply
-
-
Laboratories
-
Lightweight tubing for air and gas control
-
8. How to Choose the Right Spiral Hose
When selecting a spiral pneumatic hose, consider:
-
Inner Diameter (ID)
-
Determines airflow capacity
-
Match with tool requirements (e.g., impact wrench needs larger ID than a blow gun)
-
-
Working Pressure
-
Check maximum operating pressure (commonly 8–15 bar)
-
Consider safety margin (burst pressure usually 3x working pressure)
-
-
Material
-
PU for flexibility
-
Nylon for durability
-
PE for cost efficiency
-
-
Length and Coil Size
-
Extended length vs. retracted coil size
-
Ensure comfortable reach without overstretching
-
-
End Fittings
-
BSP, NPT, or metric thread
-
Quick-connect couplers for convenience
-
-
Operating Environment
-
Oil-resistant for workshops
-
Anti-static for electronics
-
Food-grade for clean industries
-
9. Common Problems with Spiral Hoses and How to Fix Them
-
Air Leaks at Fittings
-
Cause: worn-out threads or O-rings
-
Fix: replace seal or fitting
-
-
Kinking Near Connectors
-
Cause: frequent bending at hose ends
-
Fix: use protective spring guards
-
-
Loss of Coil Memory
-
Cause: overstretching repeatedly
-
Fix: replace hose; avoid pulling beyond rated length
-
-
Cracks or Wear
-
Cause: abrasion or chemical exposure
-
Fix: choose material suited for environment (PU for abrasion, nylon for oil)
-
10. Maintenance Tips
-
Avoid pulling hoses beyond their designed stretch length
-
Store in a clean, dry place when not in use
-
Inspect regularly for leaks, cracks, or damaged fittings
-
Use hose reels or holders to extend service life
-
Replace damaged sections immediately to avoid system failure
11. Comparison Table: PU vs Nylon vs PE Spiral Hoses
| Feature | PU (Polyurethane) | Nylon (PA) | PE (Polyethylene) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flexibility | Excellent | Moderate | Low |
| Strength | Good | Excellent | Moderate |
| Abrasion Resistance | Excellent | Good | Fair |
| Weight | Very light | Light | Light |
| Pressure Capacity | Medium | High | Low to Medium |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher | Low |
| Applications | Tools, workshops | Industry, auto | General, budget use |
12. Future Trends in Pneumatic Spiral Hoses
-
Hybrid Materials: Combining PU and nylon for balanced performance
-
Eco-Friendly Designs: Biodegradable or recyclable materials
-
Integrated Safety Features: Anti-kink and burst protection layers
-
Smart Hoses: Embedded sensors to monitor air pressure and leaks
Conclusion
Pneumatic spiral hoses may look simple, but they are essential for ensuring safe, flexible, and efficient air delivery. Choosing the right type depends on your specific application:
-
PU spiral hoses for flexibility and ergonomics
-
Nylon spiral hoses for heavy-duty, high-pressure environments
-
PE spiral hoses for lightweight and economical use
With proper selection and maintenance, spiral hoses can last for years, improving both productivity and safety in your pneumatic systems.
 Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt
